Table of Contents
Introduction
How Does Bursitis Happen?
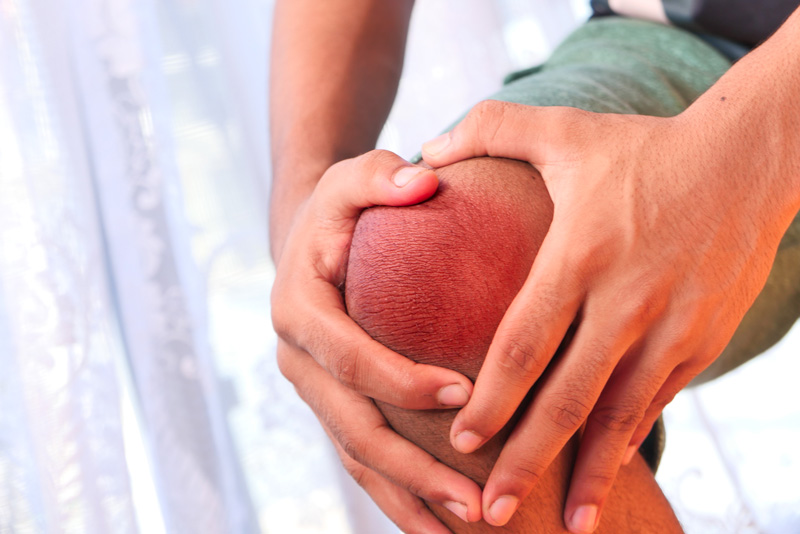
How Do I Know if I Have Knee Bursitis?
Common signs of knee bursitis include:
- Swelling on the front, inside, or back of the knee
- Pain when kneeling, bending, or applying pressure to the knee
- Warmth or redness over the swollen area
- Stiffness or discomfort with movement
- Tenderness to touch at the affected spot
A medical evaluation, often a physical exam and sometimes imaging or fluid tests, can confirm the diagnosis.
Treatments for Knee Bursitis
Most cases improve with conservative care, such as:
- Rest and avoiding activities that irritate the knee
- Ice and compression to reduce swelling
- Anti-inflammatory medications as recommended by your provider
- Physical therapy to improve flexibility and reduce strain on the knee
- Protective pads or braces to reduce pressure during activities
- Corticosteroid injections, which may be used for persistent inflammation
In rare cases, such as infection or severe, recurring bursitis, additional procedures or drainage may be needed.
References
Aaron DL, Patel A, Kayiaros S, Calfee R. Four Common Types of Bursitis: Diagnosis and Management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19(6):359-367. doi:10.5435/00124635-201106000-00006.
Brown OS, Smith TO, Parsons T, Benjamin M, Hing CB. Management of Septic and Aseptic Prepatellar Bursitis: A Systematic Review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022;142(10):2445-2457. doi:10.1007/s00402-021-03853-9.
Baumbach SF, Lobo CM, Badyine I, Mutschler W, Kanz KG. Prepatellar and Olecranon Bursitis: Literature Review and Development of a Treatment Algorithm. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(3):359-370. doi:10.1007/s00402-013-1882-7.
Looking to schedule an appointment with a physician?
Schedule an appointment with us by calling now or by clicking the button below to begin requesting your appointment today!