Table of Contents
What Is Brachymetatarsia?
Brachymetatarsia is a rare foot condition in which one or more metatarsal bones (the long bones in the foot) are abnormally short, leading to a shorter toe. This typically affects the fourth toe, which may appear raised or misaligned compared to the others. The condition can cause discomfort, difficulty wearing shoes, and aesthetic concerns.
At University Foot & Ankle Institute, our specialists offer advanced treatment options to help restore foot function and improve confidence in those affected by brachymetatarsia.
What Causes Brachymetatarsia?
Brachymetatarsia is primarily a developmental condition, meaning the affected bone stops growing too soon. It can be caused by several factors, including:
- Genetic Predisposition: Often runs in families and can be linked to hereditary traits.
- Growth Plate Closure: If the growth plate in a metatarsal bone closes too early, the bone will not develop normally.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions affecting bone development, such as Turner syndrome or pseudohypoparathyroidism, can lead to brachymetatarsia.
- Trauma or Injury: In rare cases, previous foot trauma can damage a growth plate, leading to a shortened metatarsal.
- Congenital Abnormalities: Some individuals are born with brachymetatarsia due to abnormalities in skeletal development.
Symptoms of Brachymetatarsia
While some people experience little to no discomfort, others may face significant issues, including:
- Visibly Shorter Toe: The most noticeable symptom is a toe that appears unusually short or raised.
- Pain or Discomfort: Due to uneven weight distribution, leading to pressure points and irritation.
- Difficulty Wearing Shoes: The raised or misaligned toe can rub against footwear, causing discomfort or calluses.
- Altered Foot Function: Some individuals experience balance issues or difficulty walking due to improper weight distribution.
- Psychological Concerns: Many patients seek treatment due to aesthetic concerns, as the condition can affect confidence and self-esteem.
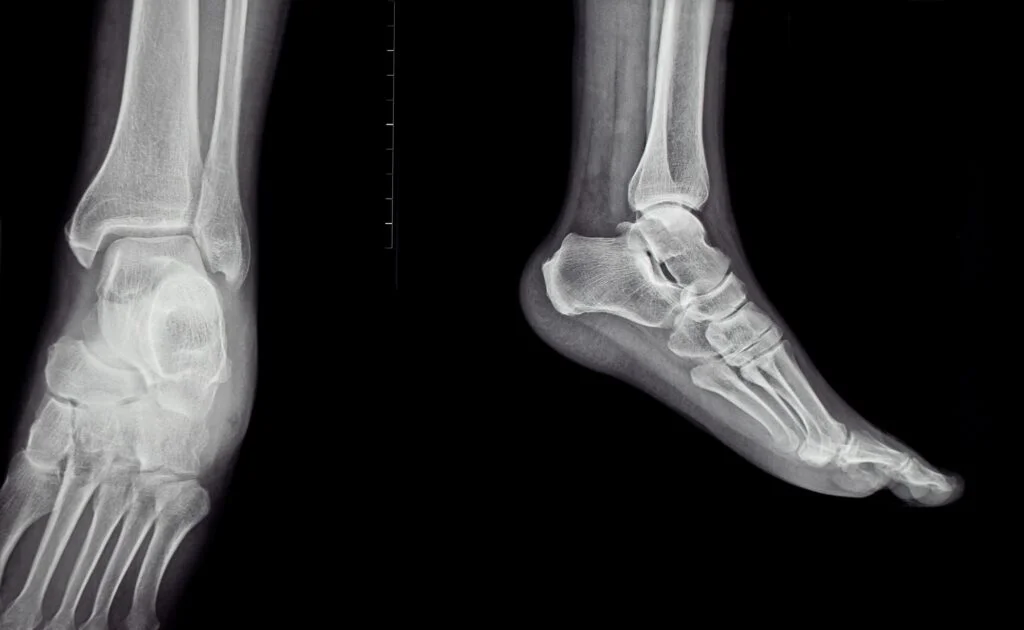
Diagnosing Brachymetatarsia
Physical Examination
X-Rays and Imaging
- X-rays provide detailed images of the metatarsal bones to confirm the diagnosis and assess severity.
- 3D imaging or CT scans may be used for surgical planning in severe cases.
Treatment Options for Brachymetatarsia
Non-Surgical Treatments
Mild cases of brachymetatarsia may be managed with conservative treatments, though they do not correct the shortened bone.
- Orthotics and Padding
- Custom orthotics can help redistribute weight across the foot to reduce pressure on the affected area.
- Padding and cushioned footwear can prevent discomfort from rubbing and irritation.
- Physical Therapy
- Stretching and strengthening exercises may improve foot function and reduce strain on adjacent toes.
Surgical Treatments
For patients seeking functional or cosmetic correction, surgical intervention is the most effective solution.
- Bone Lengthening (Callus Distraction)
- This procedure involves gradual bone lengthening using an external fixator.
- A controlled cut is made in the metatarsal bone, and the fixator gradually pulls the bone apart, encouraging new bone growth.
- The process typically takes several weeks to months, depending on the desired length.
- Bone Grafting
- A bone graft (from the patient or a donor) is used to lengthen the metatarsal.
- This method provides a quicker correction than callus distraction but may involve longer recovery times.
- Implant Surgery
- In some cases, an implant may be inserted to extend the metatarsal bone without the need for external fixation.
Recovery and Post-Treatment Care
Recovery times vary depending on the surgical method used. Patients can expect:
- Non-weight-bearing for several weeks with crutches or a walking boot.
- Physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
- Regular follow-ups to monitor bone healing and foot function.
Can Brachymetatarsia Be Prevented?
Why Choose University Foot & Ankle Institute?
At University Foot & Ankle Institute, we offer state-of-the-art diagnostic tools, advanced surgical techniques, and personalized treatment plans for brachymetatarsia. Our experienced team is committed to helping patients achieve optimal foot function and confidence.
If you are experiencing discomfort or are concerned about the appearance of your toes, schedule a consultation today to explore the best treatment options for your needs.
Dr. Gina Nalbandian specializes in reconstructive and revisional foot and ankle surgery, foot and ankle trauma, sports medicine, lapiplasty, and limb salvage.
While an undergrad, Gina volunteered at free clinics, hospitals and with the AIDS Project in Los Angeles, all the while exploring various careers in medicine. She also conducted and published her research in the lab on campus. “I soon found out that the lab life wasn’t for me, and I wanted a more hands-on approach to medicine,” she says.
Dr. Nalbandian did her residency at St. Elizabeth’s Medical Center in Boston, which is affiliated with Tufts University. As a resident, she served an academic coordinator and chief resident.
A resident of Sherman Oaks, Gina continues to volunteer her expertise with the Special Olympics, Happy Feet (providing foot care at homeless shelters), and the Boston Marathon.